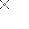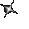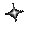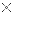
Now let's examine some of the basic instructions is greater detail to see more about what each one does.
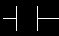 . This is used when an input signal is needed to be present for the symbol to turn on. When the physical input is On we can say that the instruction is True. We examine the input for an on signal. If the input is physically on then the symbol is on. An on condition is also referred to as a logic(1) state. This symbol normally can be used for internal inputs, external inputs and external output contacts. Remember that internal relays don't physically exist. They are simulated(software) relays.
. This is used when an input signal is needed to be present for the symbol to turn on. When the physical input is On we can say that the instruction is True. We examine the input for an on signal. If the input is physically on then the symbol is on. An on condition is also referred to as a logic(1) state. This symbol normally can be used for internal inputs, external inputs and external output contacts. Remember that internal relays don't physically exist. They are simulated(software) relays.
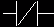 . This is used when an input signal does not need to be present for the symbol to turn on. When the physical input is Off we can say that the instruction is True. We examine the input for an off signal. If the input is physically off then the symbol is on. An off condition is also referred to as a logic(0) state. This symbol normally can be used for internal inputs, external inputs and sometimes external output contacts. Remember again that internal relays don't physically exist. They are simulated(software) relays. It is the exact opposite of the Load instruction.
. This is used when an input signal does not need to be present for the symbol to turn on. When the physical input is Off we can say that the instruction is True. We examine the input for an off signal. If the input is physically off then the symbol is on. An off condition is also referred to as a logic(0) state. This symbol normally can be used for internal inputs, external inputs and sometimes external output contacts. Remember again that internal relays don't physically exist. They are simulated(software) relays. It is the exact opposite of the Load instruction.
| Logic State | Load | LoadBar |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | False | True |
| 1 | True | False |
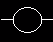 .When there is a path of True instructions preceding this on the ladder rung, it will also be True. When the instruction is True it is physically On. We can think of this instruction as a normally open output. This instruction can be used for internal coils and external outputs.
.When there is a path of True instructions preceding this on the ladder rung, it will also be True. When the instruction is True it is physically On. We can think of this instruction as a normally open output. This instruction can be used for internal coils and external outputs.
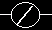 . When there is a path of False instructions preceding this on the ladder rung, it will be True. When the instruction is True it is physically On. We can think of this instruction as a normally closed output. This instruction can be used for internal coils and external outputs.
It is the exact opposite of the Out instruction.
. When there is a path of False instructions preceding this on the ladder rung, it will be True. When the instruction is True it is physically On. We can think of this instruction as a normally closed output. This instruction can be used for internal coils and external outputs.
It is the exact opposite of the Out instruction.| Logic State | Out | OutBar |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | False | True |
| 1 | True | False |